Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy in Varanasi

Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy focuses on diagnosing, treating, and preventing disorders related to muscles, bones, joints, tendons, and ligaments. Whether it’s due to injury, poor posture, repetitive strain, or underlying conditions, these issues can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
At Dr. Satyam Pain & Health Care Clinic in Varanasi, we offer specialized Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy aimed at reducing pain, restoring movement, and enhancing overall physical function without relying on surgical methods.
What is Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy?
Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy focuses on diagnosing, treating, and preventing disorders related to muscles, bones, joints, tendons, and ligaments. Whether it’s due to injury, poor posture, repetitive strain, or underlying conditions, these issues can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
At Dr. Satyam Pain & Health Care Clinic in Varanasi, we offer specialized Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy aimed at reducing pain, restoring movement, and enhancing overall physical function without relying on surgical methods.
Our Treatment Methods Include:
- Manual Therapy: Specialized hands-on techniques to relieve muscle tension, improve joint mobility, and enhance alignment.
- Electrotherapy: Effective methods like TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and IFT (Interferential Therapy) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Rehabilitation Exercises: Tailored exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and restore movement.
Posture Correction: Guidance to correct postural habits that contribute to musculoskeletal pain.
Benefits of Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy
- Pain Relief: Physiotherapy helps to manage and reduce pain through hands-on treatments, exercises, and modalities such as heat, ice, and electrical stimulation.
- Improved Mobility: It helps restore mobility and flexibility in joints and muscles, making it easier to perform daily activities.
- Post-Injury Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy speeds up recovery time after injuries by strengthening muscles and restoring function to injured areas.
- Enhanced Strength and Stability: Specific exercises are prescribed to strengthen the muscles surrounding injured or weak joints, reducing the likelihood of future injury.
- Prevention of Future Injuries: Physiotherapists help teach you techniques and exercises that can prevent future musculoskeletal problems.
Why Choose Dr. Satyam Jaiswal?
We provide a personalized, patient-centered approach to Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy, ensuring you receive the right care based on your specific needs.
Book Your Consultation Today
If you’re looking for expert Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy in Varanasi, visit Dr. Satyam’s Pain & HealthCare Clinic for advanced care and personalized treatment.
📞 Contact us now to book your consultation and take the first step toward pain-free living!
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is a crucial ligament in the knee that provides stability and controls movement. It connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia), preventing excessive forward motion and rotation of the knee joint. ACL injuries are common in athletes, especially those involved in high-impact sports like football, basketball, and skiing. A torn ACL can cause pain, swelling, and instability, often requiring surgical reconstruction followed by rehabilitation to restore strength and mobility. Preventive measures like proper warm-ups, strengthening exercises, and wearing supportive gear can help reduce the risk of ACL injuries.
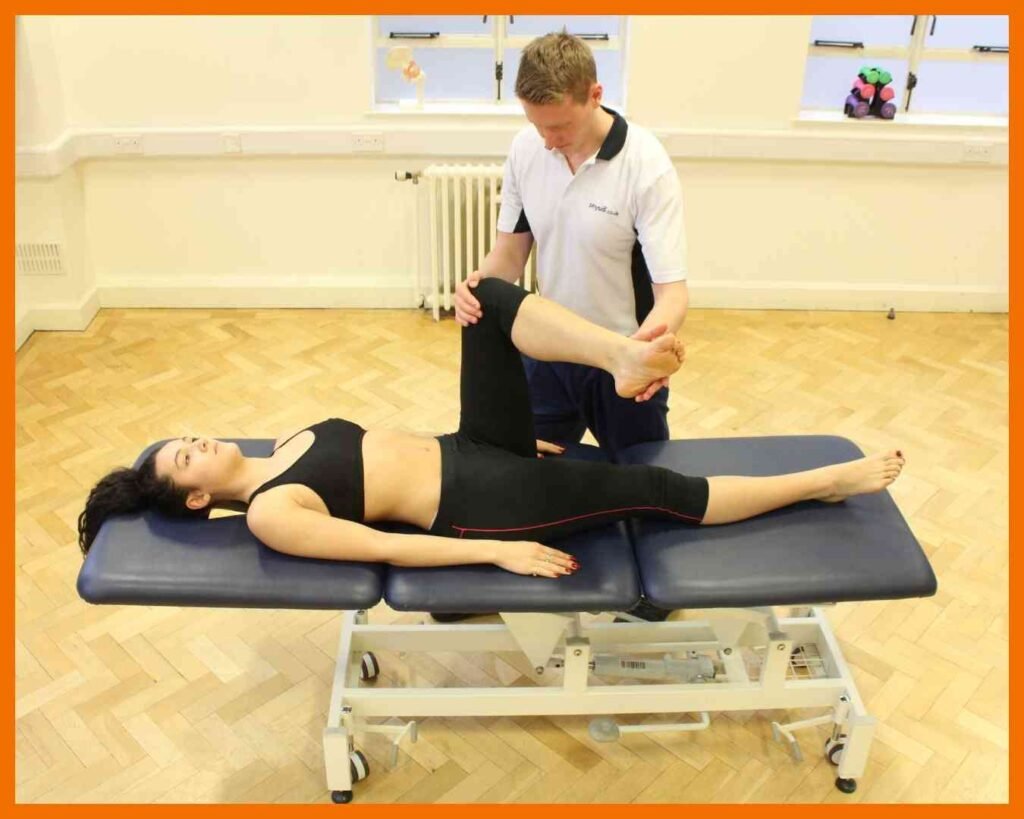
Back Pain
Back pain is a common condition that can result from poor posture, muscle strain, injury, or underlying health issues like arthritis or disc problems. It can cause discomfort ranging from mild stiffness to severe pain that limits movement. Treatment options depend on the cause and severity but often include rest, gentle stretching, physical therapy, and pain management techniques like heat therapy or medication. Maintaining good posture, staying active, and strengthening core muscles can help prevent back pain and improve spinal health, ensuring better mobility and overall well-being.

Shoulder Impingement
Shoulder Impingement occurs when the rotator cuff tendons are compressed between the shoulder bones, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. This condition is common among athletes and individuals who perform repetitive overhead movements, such as swimmers, painters, and weightlifters. Symptoms include shoulder pain, weakness, and difficulty reaching behind the back. Treatment typically involves rest, physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and posture correction to relieve pressure on the tendons. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be needed to restore full function and prevent long-term damage.

Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar Fasciitis is a common foot condition that causes heel pain due to inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes. It typically develops from excessive strain, prolonged standing, improper footwear, or high-impact activities like running. Symptoms include sharp pain in the heel, especially in the morning or after long periods of inactivity. Treatment involves rest, stretching exercises, proper footwear, and anti-inflammatory medications. In severe cases, physical therapy, orthotic support, or corticosteroid injections may be recommended to relieve pain and restore mobility.
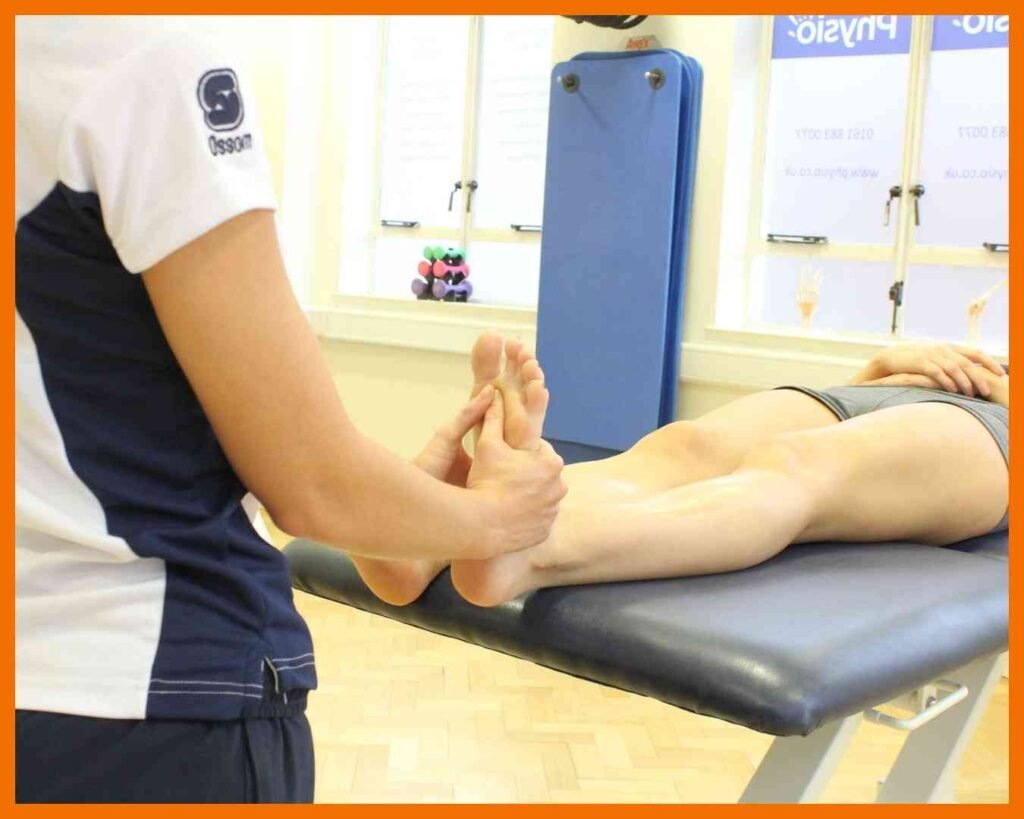
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the spine, leading to pain and stiffness. Over time, the inflammation can cause the vertebrae to fuse, resulting in a rigid, less flexible spine. The exact cause is unknown, but genetic factors, especially the presence of the HLA-B27 gene, play a significant role. Symptoms often start in the lower back and pelvis, progressing to other parts of the spine and joints. Early signs include back pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Treatment focuses on managing pain, improving posture, and preventing joint damage through medications like NSAIDs, biologics, and physical therapy. Regular exercise and stretching can help maintain flexibility and function.

Calf Strain
A calf strain is an injury to the muscles at the back of the lower leg, typically caused by overstretching or overexertion. It often occurs during activities that involve sudden acceleration, deceleration, or jumping, such as running or sports like soccer and basketball. Symptoms include pain, swelling, muscle weakness, and difficulty walking. Mild strains may heal with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.), while more severe strains may require physical therapy, stretching exercises, and in some cases, a period of immobilization. Preventing calf strain involves warming up before exercise, gradually increasing intensity, and maintaining flexibility in the calf muscles.
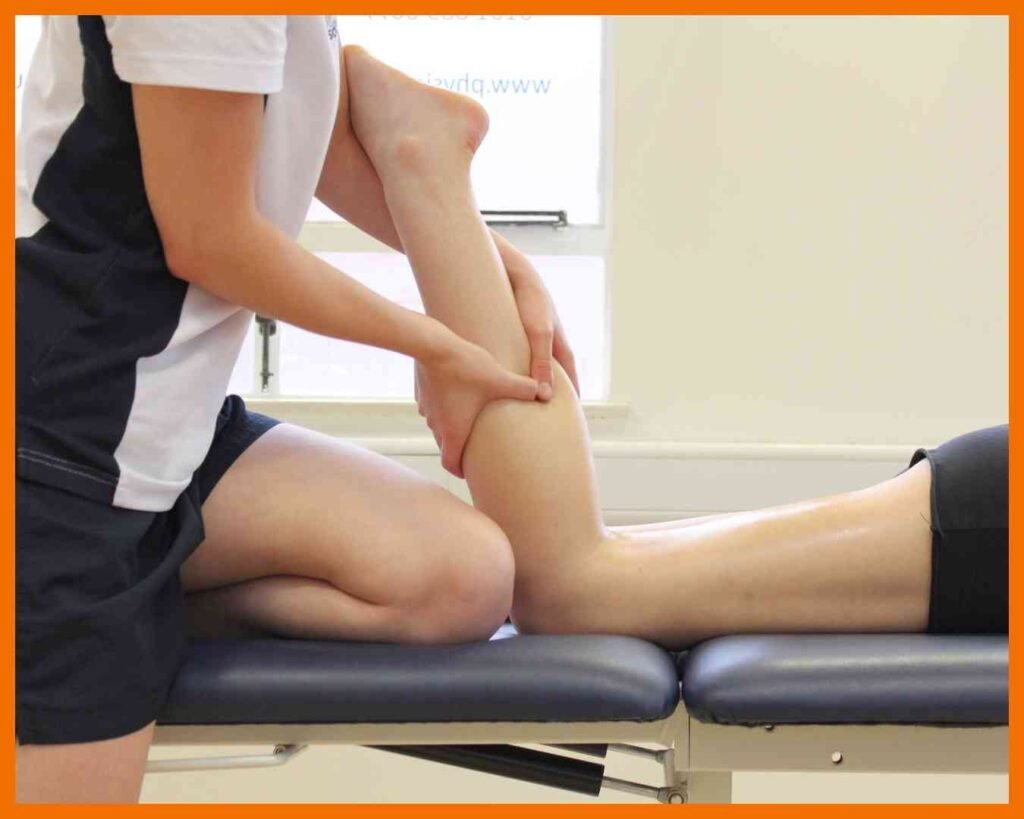
Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical Spondylosis is a degenerative condition of the cervical spine (neck) that occurs as the discs, joints, and bones in the neck wear down with age. It is commonly referred to as “neck arthritis” and can cause pain, stiffness, and in some cases, nerve compression that leads to numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or hands. The main causes include age-related changes, poor posture, or injury. Symptoms may vary from mild discomfort to chronic pain and restricted movement. Treatment usually includes pain management, physical therapy, exercises, and lifestyle changes to improve posture and flexibility. In more severe cases, surgery may be considered to relieve nerve compression and improve quality of life.

Chondromalacia Patella
Chondromalacia Patella, also known as runner’s knee, is a condition where the cartilage on the underside of the kneecap (patella) deteriorates or softens, causing pain and discomfort, especially during activities like running, squatting, or climbing stairs. It often occurs due to overuse, misalignment of the kneecap, or injury. Symptoms typically include a dull ache around or behind the kneecap, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee. Treatment focuses on rest, ice, physical therapy, and strengthening exercises for the quadriceps to improve knee alignment. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to repair or smooth the damaged cartilage.
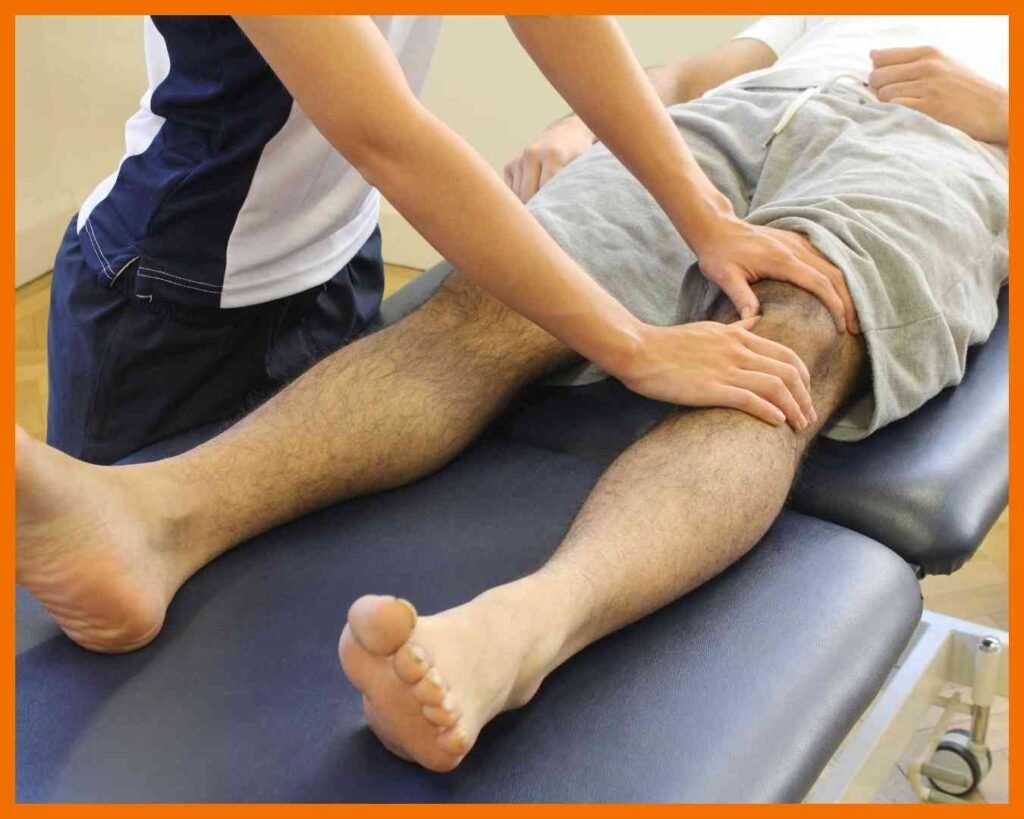
De Queruain Tenosynouitis
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a painful condition affecting the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It occurs when the tendons in the wrist become inflamed due to repetitive motion or overuse, often from activities that involve gripping or twisting, such as texting, gardening, or lifting. The inflammation causes pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the thumb or wrist, and you may experience a “sticking” sensation when moving your thumb. Treatment typically includes rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, splinting, and physical therapy. In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary to relieve pain and restore function.

Diastasis Recti
Diastasis Recti is a condition where the large abdominal muscles (rectus abdominis) separate along the midline of the body, often due to pregnancy, obesity, or intense physical exertion. This separation creates a gap in the abdominal wall, leading to a weakened core and potential issues like back pain or poor posture. It’s most common in women after childbirth, but it can affect men and women of any age or fitness level. Symptoms include a visible bulge in the abdomen, especially when straining or contracting the muscles. Treatment typically involves core strengthening exercises and physical therapy to promote muscle re-alignment. In severe cases, surgery may be recommended to repair the muscle separation.

Hip Pain
Hip Pain can arise from various causes, including arthritis, bursitis, muscle strain, or injury. It is often felt in the front, side, or deep within the hip joint and can range from mild discomfort to severe, disabling pain. Common causes include osteoarthritis, which leads to joint wear and tear, or conditions like tendonitis and bursitis, which involve inflammation in the surrounding tissues. Other factors like poor posture, overuse, or an improper walking gait can also contribute to hip pain. Treatment typically involves rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and lifestyle changes such as weight management. In more severe cases, injections or surgery may be needed to relieve pain and restore function.

Ankle sprain
An ankle sprain occurs when the ligaments that support the ankle are stretched or torn due to sudden twisting, rolling, or impact. This common injury can cause pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty in walking. Mild sprains may heal with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.), while severe cases may require medical attention, including physical therapy or bracing. Strengthening exercises and wearing proper footwear can help prevent future sprains, ensuring better stability and mobility.
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis is a condition where the spaces within the lower spine narrow, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This narrowing often occurs due to age-related changes, such as the thickening of ligaments, bone spurs, or disc degeneration. The condition can cause symptoms like lower back pain, numbness, tingling, weakness in the legs, and difficulty walking or standing for long periods. In severe cases, it can lead to loss of bladder or bowel control. Treatment options include physical therapy, medications, epidural injections, and in some cases, surgery to relieve pressure on the nerves and improve mobility.

Meniscus Injury
A meniscus injury involves damage to the meniscus, a cartilage structure in the knee that acts as a cushion between the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia). This injury often occurs during twisting motions, heavy lifting, or sports activities, such as basketball or football. Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and a feeling of the knee “locking” or “giving way.” In some cases, the injury can cause difficulty in fully straightening the knee. Treatment may involve rest, ice, compression, elevation (R.I.C.E.), physical therapy to restore strength and mobility, or in severe cases, surgery to repair or remove the damaged portion of the meniscus.
Post Fracture
Post-Fracture refers to the period following a bone fracture, during which the body heals and restores the damaged bone. After the fracture has been treated, either through casting, surgery, or immobilization, the focus shifts to rehabilitation and recovery. This includes managing pain, preventing complications like stiffness or weakness, and gradually regaining strength and mobility. Physical therapy is often crucial for improving joint flexibility and muscle strength, while proper nutrition and rest help accelerate the healing process. It’s essential to follow a doctor’s instructions carefully to ensure full recovery and avoid re-injury. In some cases, long-term follow-up care may be needed to ensure optimal bone function.

Post-Operative
Post-Operative refers to the period following a surgical procedure, during which the focus is on recovery and healing. This phase typically involves managing pain, preventing infection, and monitoring for any complications that may arise after surgery. The healthcare team provides instructions on wound care, medication, and physical activity to promote healing. Rehabilitation, including physical therapy or exercises, may also be recommended to regain strength and mobility, depending on the type of surgery. It’s essential to follow the doctor’s guidelines carefully to ensure a smooth recovery and avoid setbacks. Regular follow-up appointments are often scheduled to assess progress and address any concerns.

Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine, often forming an “S” or “C” shape. It can occur at any age but is most commonly diagnosed in adolescents during growth spurts. The cause is often unknown, though it may result from genetic factors, neuromuscular conditions, or injury. Symptoms can include uneven shoulders or hips, back pain, and difficulty breathing in severe cases due to pressure on the lungs. Mild cases may require only observation, while more severe cases might need physical therapy, braces, or surgery to correct the curvature and prevent further complications. Regular check-ups are important for monitoring the progression of scoliosis.

Joint Dysfunction
Joint Dysfunction refers to abnormal movement or misalignment of a joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. It can affect any joint in the body, including the spine, hips, knees, shoulders, and wrists. Common causes include injury, overuse, arthritis, or muscle imbalances that affect the proper function of the joint. Symptoms may include swelling, pain during movement, and difficulty performing everyday tasks. Treatment for joint dysfunction typically involves physical therapy to improve strength and mobility, pain management through medication or injections, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise can also help prevent joint dysfunction and manage symptoms.
Supraspinatus Tendinitis
Supraspinatus Tendinitis is an inflammation of the supraspinatus tendon, which is one of the four tendons that make up the rotator cuff in the shoulder. This condition typically occurs due to overuse or repetitive movements, especially activities involving overhead motions such as swimming, throwing, or weightlifting. It can cause pain and tenderness in the shoulder, particularly when lifting the arm or reaching overhead. Other symptoms include weakness and limited range of motion. Treatment often includes rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding muscles and restore movement. In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary.

Trigger Finger
Trigger Finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, is a condition where one of your fingers or thumbs gets stuck in a bent position and then suddenly pops straight. It occurs when the tendons in the finger become inflamed, usually due to repetitive gripping actions or underlying conditions like arthritis or diabetes. The inflammation makes it difficult for the tendon to slide smoothly through its sheath, causing the finger to catch or lock. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and a popping or snapping sensation when moving the finger. Treatment options include rest, splinting, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery if the condition persists or worsens.

Tendonitis
Tendonitis is the inflammation or irritation of a tendon, which is the thick fibrous cord that attaches muscle to bone. It typically occurs due to repetitive motion or overuse, especially in activities that involve intense physical exertion, such as sports or manual labor. Common areas affected by tendonitis include the shoulder (rotator cuff tendonitis), elbow (tennis elbow), wrist, knee (patellar tendonitis), and Achilles tendon. Symptoms include pain, tenderness, swelling, and limited movement around the affected area. Treatment often involves rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and in some cases, corticosteroid injections. If the condition becomes chronic or severe, surgical intervention may be required to repair the tendon.
Arthroplasty
Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring the function of a joint by removing damaged or arthritic bone and replacing it with a prosthetic implant. The most common type of arthroplasty is joint replacement, typically performed on the hip, knee, or shoulder. It is recommended for patients with severe joint pain, stiffness, and loss of function due to conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic joint injuries. The procedure can significantly reduce pain and improve mobility, allowing individuals to return to daily activities. Recovery time varies, but physical therapy is often necessary to regain strength, flexibility, and function in the joint. In some cases, less invasive arthroscopic procedures may be used to repair joint issues.
Frozen Shoulder
Frozen Shoulder (also known as adhesive capsulitis) is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint, which leads to a limited range of motion. It typically develops gradually in three stages: freezing, frozen, and thawing. In the freezing stage, pain begins to increase as the shoulder becomes stiffer. In the frozen stage, the pain may decrease, but the shoulder remains very stiff, making movement difficult. In the thawing stage, the range of motion slowly improves. The exact cause of frozen shoulder is often unknown, but it can be related to factors like injury, surgery, or certain medical conditions such as diabetes. Treatment often includes physical therapy to improve mobility, anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases, surgery to release the tightened capsule around the shoulder joint.
SI Joint Dysfunction
SI Joint Dysfunction refers to problems with the sacroiliac (SI) joint, which connects the lower spine (sacrum) to the pelvis (iliac bones). Dysfunction occurs when there is either too much or too little movement in the SI joint, leading to pain and discomfort. It is often caused by injury, pregnancy, arthritis, or postural issues that affect the alignment of the spine and pelvis. The pain is typically felt in the lower back, buttocks, or hips and may radiate down the legs. Other symptoms include stiffness and difficulty in movements like bending or walking. Treatment usually includes physical therapy to strengthen and stabilize the pelvis, anti-inflammatory medications for pain relief, and lifestyle adjustments. In some cases, injections or surgery may be considered to address severe or chronic SI joint dysfunction.

Slipped Disc
A slipped disc, also known as a herniated disc or disc prolapse, occurs when one of the rubbery cushions (discs) between the bones of the spine (vertebrae) slips out of its normal position or ruptures. This can result in the inner gel-like substance of the disc leaking out, potentially pressing on nearby nerves and causing pain, numbness, or weakness. A slipped disc typically affects the lower back (lumbar spine) or neck (cervical spine), but can occur anywhere along the spine. Common symptoms include sharp or radiating pain, tingling sensations, muscle weakness, and difficulty moving. The condition is often caused by aging, repetitive strain, or sudden trauma, such as lifting heavy objects. Treatment usually involves rest, pain management (e.g., anti-inflammatory medications), physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgical intervention if conservative measures don’t relieve symptoms.

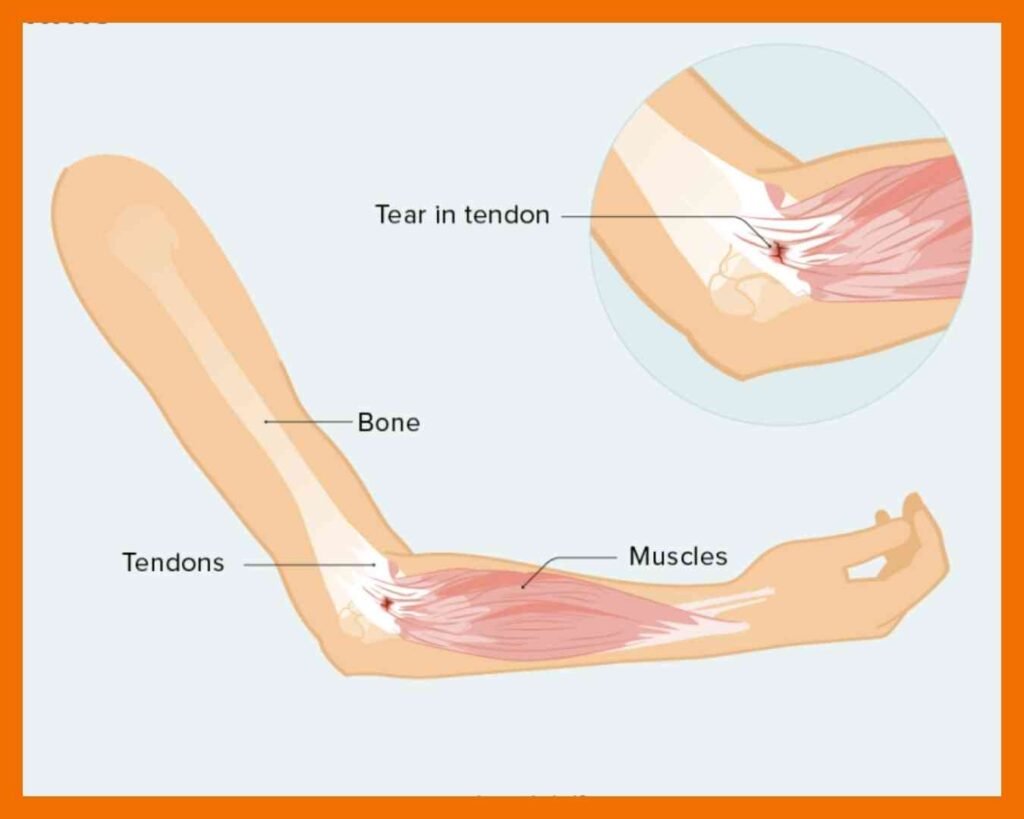
Tennis Elbow and Golfer’s Elbow
Tennis Elbow (lateral epicondylitis) affects the outer part of the elbow and is usually caused by overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons, particularly through repetitive motions such as gripping or swinging a tennis racket. Symptoms include pain and tenderness on the outer elbow, which may radiate down the forearm, and weakness in the hand or wrist.
Golfer’s Elbow (medial epicondylitis) occurs on the inner side of the elbow and is typically caused by repetitive motions that involve gripping and swinging, such as golfing or throwing. Symptoms include pain and swelling on the inner elbow, which may extend into the forearm, as well as difficulty bending the arm or gripping objects.

Sciatica
Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back through the hips, buttocks, and down each leg. The condition typically occurs when the sciatic nerve is irritated or compressed, often due to a herniated disc, bone spurs, or narrowing of the spine (spinal stenosis). The primary symptom is sharp or shooting pain, usually on one side of the body, but it can also include numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected leg. While sciatica often improves with conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, pain relief medications, and stretching exercises, severe cases may require more advanced treatments, such as injections or surgery, especially if the nerve compression causes significant muscle weakness or loss of bladder control.

Total Knee Replacement
Trigger Point Pain refers to localized, tight knots or areas of muscle tissue that are hypersensitive and can cause discomfort or pain, often radiating to other areas of the body. These points are commonly found in muscles, particularly in the neck, shoulders, back, and thighs. Trigger points can develop due to muscle overuse, poor posture, stress, or injury, and are frequently associated with conditions like myofascial pain syndrome.
The pain caused by trigger points can be sharp or dull and may worsen with movement or pressure. Common symptoms include tenderness at the site of the trigger point and referred pain, where pain is felt in a different area of the body. Treatment typically includes physical therapy, massage therapy, dry needling, stretching exercises, and the use of heat or ice to alleviate muscle tension and reduce pain. In some cases, medications or injections may be used to relax the muscle and relieve pain.
Trapezitis
Trapezitis is the inflammation of the trapezius muscle, which is a large muscle that extends down the back of the neck and upper spine to the middle of the back. It plays a significant role in moving and stabilizing the shoulder blades and supporting neck movement. Trapezitis typically occurs due to overuse, poor posture, muscle strain, or stress. It can also be a result of injury or repetitive activities such as sitting at a desk for extended periods, carrying heavy loads, or engaging in activities that require prolonged shoulder movement.
Symptoms of trapezitis include neck and shoulder pain, tenderness along the trapezius muscle, stiffness, headaches, and a restricted range of motion in the neck and upper back. Treatment generally involves rest, applying heat or ice to the affected area, physical therapy to improve posture and flexibility, massage therapy, and pain relief medications. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or other medical interventions may be required.

Trigger Point Pain
Trigger Point Pain, also known as Myofascial Trigger Point Pain, is a condition caused by tight, knotted muscles that create localized pain and tenderness. These trigger points can develop due to muscle overuse, poor posture, stress, or injury, leading to referred pain in other areas of the body.
Common symptoms include muscle stiffness, tenderness, and radiating pain that worsens with movement or pressure. It often affects the neck, shoulders, back, and hips.
Treatment focuses on massage therapy, stretching, physical therapy, dry needling, and trigger point injections to relieve muscle tension. Heat therapy, relaxation techniques, and posture correction can also help manage and prevent trigger point pain.

Frequently Asked Questions
Dr. Satyam at Satyam Pain Healthcare is a trusted specialist in musculoskeletal physiotherapy, providing advanced treatments for muscle and joint pain.
It helps with conditions like arthritis, frozen shoulder, knee pain, back pain, sports injuries, muscle stiffness, and post-surgical recovery.
Yes! Regular physiotherapy sessions, combined with customized exercises, manual therapy, and lifestyle changes, can significantly reduce chronic pain and improve mobility.
The number of sessions varies depending on the severity of the condition. Many patients experience improvement within 4-6 weeks, but long-term cases may require continued therapy.
